CT Scan
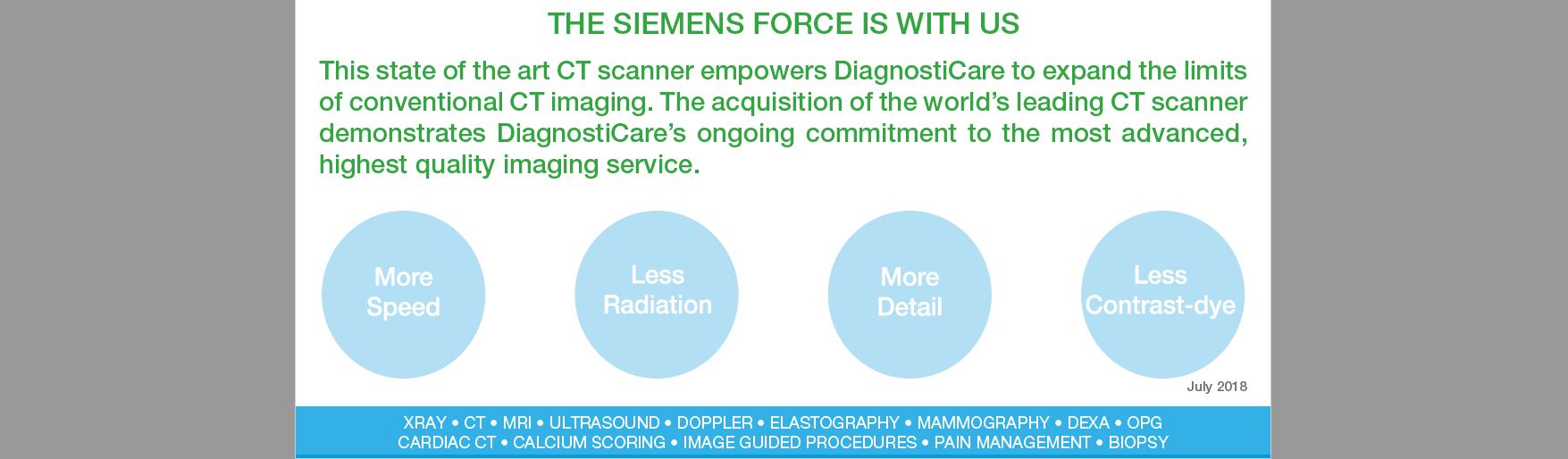
Diagnosticare has taken ownership of the worlds best CT scanner.
Siemens Force is the industries leading scanner for radiation dose and detail.
Don’t be fooled by the labels “Low Dose CT Scanning”.
This is the lowest dose CT scanner available. Diagnosticare is always willing to put patient welfare before cost saving.
Definition
A computed tomography (CT) scan is an imaging study that uses x-rays to create cross-sectional images of the body.
Other names/synonyms
CAT scan; Computed tomography scan.
How the test is performed
You will be escorted into the CT room and asked to lie on a narrow table that slides into the aperture of the CT scanner. Depending on the study being done, you may need to lie on your stomach or back.
In most scans your head is positioned outside of the scanner aperture.
Once you are in position and unbeknownst to you, the machine’s x-ray tube rotates around you.
Small detectors inside the scanner measure the amount of x-rays that make it through the part of the body being studied. A computer takes this information and uses it to create several individual images, called slices. These images can be stored, viewed on a monitor, or printed on film. Three-dimensional images of organs can be created by stacking the individual slices together.
You must keep still during the exam, because movement causes blurring of the images. You may be told to hold your breath for short periods of time.
Generally, complete scans take only a few minutes. The newest multi-detector scanners can image your entire body, head to toe, in less than 30 seconds.
How to prepare for the test
Certain tests require a special fluid called contrast to be delivered into a vein before the test starts. Contrast can highlight specific areas inside the body, which creates a clearer image.
Some people have allergies to IV contrast and may need to take medications before their test in order to safely receive this substance.
You will be asked about any allergies you may have prior to commencement of the scan.
Contrast can be given several ways and depends on the type of CT being performed.
- It may be delivered through a vein (IV) in the back of your hand or your forearm.
- It may be given through the rectum using an enema.
- You might drink the contrast before your scan.
Whether you need to drink the contrast depends on the type of exam being done. The contrast liquid is clear and tasteless. The contrast eventually passes out of your body through your stools.
If contrast is used, you may also be asked not to eat or drink anything for 4-6 hours before the test.
If you weigh more than 150 kilograms, have your doctor contact the radiographer before the exam. CT scanners have a weight limit. Too much weight can cause damage to the scanner’s working parts.
Since x-rays have difficulty passing through metal, you will be asked to remove jewelry and wear a hospital gown during the study.
How the test will feel
Some people may have minor discomfort from lying on the hard table.
Contrast given through an IV may cause a slight warm or hot sensation, a metallic taste in the mouth, and a warm flushing of the body. These sensations are normal and usually go away within a few seconds
Why the test is performed
CT creates high quality pictures of the body, including the brain, chest, spine, and abdomen. CT may be used to:
- Guide the radiologist to the right area during a biopsy or injection
- Identify masses and tumours including cancer
- Study blood vessels
What the risks are
CT scans and other x-rays are strictly monitored and controlled to make sure they use the least amount of ionising radiation. CT scans do create low levels of ionising radiation, which has the potential to cause cancer and other defects. However, the risk associated with any individual scan is very small. The risk increases as numerous additional studies are performed.
In some cases, a CT scan may still be done if the benefits substantially outweigh the risks. For example, it can be more risky not to have the exam, especially if your doctor thinks you might have cancer.
An abdominal CT is usually not recommended for pregnant women, because it may harm the unborn child. Women who are or may be pregnant should speak with their doctor to determine if ultrasound can be used instead.
The most common type of contrast given into a vein contains iodine. If a person with an iodine allergy is given this type of contrast, nausea, sneezing, vomiting, itching or hives may occur.
If you absolutely must be given such contrast, your doctor may choose to treat you with antihistamines (such as Benadryl) or steroids before the test.
The kidneys help filter the iodine out of the body. Therefore, if you have kidney disease or diabetes you should receive plenty of fluids after the test and be closely monitored for kidney problems. If you have diabetes or are on kidney dialysis, talk to your radiographer before the test about your risks.
Rarely, the contrast may cause a life-threatening allergic response called anaphylaxis. If you have any trouble breathing during the test you should notify the radiographer immediately. Scanners come with an intercom and speakers so the radiographer can hear you at all times.
CT Colonography
CT colonography, also known as virtual colonoscopy is as effective, less invasive and quicker to perform then endoscopic (fibreoptic) colonoscopy in detection of colon cancer in screening programmes. Unlike endoscopic colonoscopy, no sedation is required which allows you to drive and or go back to work after the procedure. DiagnostiCare offers you access to latest generation CT technology — the 64-slice CT scanner — for this screening. Centers offering CT colonoscopy have specialised software programmes and specially certified radiologists to read the results. CT colonoscopy is indicated if:
- You require colon cancer screening because you’re age 50 or older or because you have family history of cancers. (not Medicare rebatable)
- If you have vague symptoms, suggesting that a polyp may be present (anaemia from blood loss in the stool) (Not currently Medicare rebatable)
- You have had a failed endoscopic colonoscopy (Medicare rebatable)
Benefits of Virtual Colonoscopy
Benefits of virtual colonoscopy include:
- Low risk: Unlike colonoscopy, CT colonoscopy lacks the risks associated with sedation and with bowel perforation.
- Faster: CT colonoscopy takes about an hour to perform, as opposed to the majority of the day required for endoscopic colonoscopy. Patients can return to work and normal daily activities on the same day and do not need someone to take them home.
- Quick diagnosis: At Diagnosticare, reports are returned to your doctor within 48 hours or sooner.
- We can see what is in, and outside the bowel wall: Unlike endoscopic colonoscopy, CT colonoscopy can detect the cancers and growths in and outside the colon because it images the entire abdominal cavity and pelvis. CT colonoscopy is approved by the American Cancer Society (ACS) and leading gastrointestinal societies as an alternative to endoscopic colonoscopy.
What Happens During the Procedure
Virtual colonoscopy requires the same preparation as standard colonoscopy. You must receive laxative bowel cleansing and a liquid only diet for 24 hours prior to the scan. You will also be asked to swallow a mouthful of Barium the night before the study. Detailed preparation instructions are available on booking. The procedure involves placing a small rubber tube (compared to a 2 meter scope used in endoscopic colonoscopy) into the rectum to inflate the colon. The radiologist inserts some carbon dioxide into the colon to expand it. Carbon dioxide which provides better visualisation is more rapidly absorbed and causes much less cramping and discomfort compared with room air. You are given an antispasmodic (Buscopan) immediately prior to insufflation of the Carbon Dioxide. The scan takes 10 to 12 seconds on your back and the same time when lying on your stomach. The whole procedure takes about one hour. If a polyp or polyps are found, then endoscopic colonoscopy must be performed to remove them. You’ll have to complete another bowel preparation, usually on a different day. Polyps are detected in about 10 to 20 percent of patients at colonoscopy.
Cardiac CT
Definition
CT Coronary Angiography is the x-ray examination of the blood vessels of the heart after contrast has been injected into the bloodstream. (Contrast is a water-soluble substance that improves the visibility of internal structures and is usually harmless to the body). Accurate information is obtained without the need to position a catheter in the coronary arteries. Information is also obtained about the heart muscle and heart valves. CT Coronary Angiography allows for detection of calcified and soft, non-calcified narrowing and blockage of the coronary arteries. It is also useful in following progress of coronary artery stents.
How to prepare for the test
Every patient is different, so preparation will vary. The best images are acquired with slower heart rates. So, patients need to avoid any stimulants (Nicotine caffeine etc) no smoking or drinking alcohol or soft drinks containing caffeine 24 hours before your appointment. Patients that are currently taking preventative asthma medication will need to visit our practice at least 2 days before their appointment.. Most patients will arrive 75 minutes before their scan to fill our paperwork and administration of a beta blocker (metoprolol) to lower heart rate.
Procedure
A plastic IV access cannula will be placed in a vein and you will be positioned on the scanner. ECG leads will be attached to your chest. You may receive an under the tongue spray just before the scan. The intravenous contrast will then be injected. This is the same contrast used for all CT scans. We then proceed with the scan.
How the test will feel
You will feel a warm flush sensation when the intravenous contrast is injected, which is normal.
Recovery
After the scan is completed, you are free to go within a few minutes.
What the risks are
The vast majority of examinations proceed smoothly. There may be a reaction to contrast medium such as wheezing and skin rash. Severe reactions however are extremely rare.
Contraindications
These are conditions or factors that serve as a reason to withhold treatment.
- Severe Asthma
- Allergy to contrast medium
- Poor renal function
- Inability to lie still
About the Referral
CT Coronary Angiography is Medicare rebatable if a physician or cardiologist makes the referral.
Calcium Scoring is an out of pocket procedure.
The radiation dose is anywhere from 1.6 millisieverts. (Annual environmental background radiation is approximately 2 millisieverts). Most studies are performed on the low dose step-and-shoot mode with dose of 1.8 to 2.5 millisieverts.
Heart disease and stroke
Heart disease and stroke is the cause of death in about half of all Australians who die each year. Many people have no warning signs of the disease when their first attack happens. Nearly half of first attack patients die from that event.
What is Artery Calcium Scoring?
The Coronary Calcium Score is a measurement of the amount of calcium in the walls of the arteries that supply the heart muscle. Calcification of the artery occurs secondary to a disease called atherosclerosis. This calcification is a reliable indicator of the overall load of atherosclerosis in a person’s arteries. The calcium score measures your risk of having a heart attack or stroke in the next five years.
A valuable preventative measure
Your doctor will use the Calcium Score to decide whether you are at low or high risk of a heart attack and use this information to reduce your risk. This may be achieved by changes in diet, increased exercise, blood pressure control, stopping smoking and reducing cholesterol.
CT Scan Clinic in Melbourne
As a leading CT Scan facility in Melbourne, we provide hi-tech CT Scan services with the highest integrity. Our state-of-the-art Siemens Force scanner delivers impressive accuracy and detail in the images captured. This modern technology is handled by expert technicians who have undergone extensive training in their respective fields, guaranteeing you get the best care available.
We constantly strive to improve our services and stay-up-to-date with the latest technological advancements, as well as industry regulations. This commitment to innovation and quality means we stand out among other radiology clinics in Melbourne.
Why Choose DiagnostiCare for a CT Scan in Melbourne?
- Cutting-edge Technology: A modern CT scanner, the Siemens Force, is at the helm of our CT scan services. This advanced scanner offers the highest precision at the lowest possible dose of radiation.
- Highly Skilled Technicians: All our radiologists and technicians have received top-tier training, ensuring you receive care that aligns with international standards.
- Bulk Billing: At DiagnostiCare, we believe healthcare should be accessible to all. That’s why we offer bulk billing to alleviate the financial burden.
- Comprehensive Care: We ensure no stone is left unturned during your CT Scan. You receive a detailed overview of the results to guide your further medical procedures.
- Personalised Attention: At DiagnostiCare, you’re not just a number but a valued client receiving personalised care.
Preparing for a CT Scan at our Melbourne Clinic
Are you nervous about your upcoming CT Scan? DiagnostiCare has put together a helpful guide to help you prepare for your CT Scan procedure. First, you should avoid any stimulants, such as nicotine or caffeine in the 24 hours before your appointment. It’s also important to inform your radiologist if you have any existing medical conditions like asthma or poor renal function.
Before your CT scan, you will fill out paperwork and may be administered a beta blocker to lower your heart rate. During the scan, you’ll lie on a narrow table that slides into the scanner. You might also be given a contrast fluid to highlight specific areas inside the body for a clearer image.
Your comfort is our primary concern. If you have any questions or need further assistance in preparation for a CT scan at our Melbourne clinic, feel free to call us on (03) 9337 8288 or email us at info@diagnosticare.com.au.
CT Coronary Angiography and Calcium Score: Why It Matters
CT Coronary Angiography, one of our key services, is an X-ray examination of the blood vessels around the heart. It provides valuable information without invasive procedures like catheter placement. Furthermore, CT Coronary Angiography and Calcium Score procedures can highlight calcium deposits in the arteries, providing a reliable indicator of atherosclerosis and signifying your risk of heart attack or stroke.
With our state-of-the-art technology and team of experienced radiologists, DiagnostiCare ensures that this procedure is safe, precise, and comfortable. Hallmarks of our service include quick diagnosis, low risk, and exceptional patient comfort.
To learn more about our CT Coronary Angiography services in Melbourne or to book an appointment, reach out to our team at DiagnostiCare today.
Frequently Asked Questions About CT Scan Melbourne
DiagnostiCare stands out for its commitment to providing high-integrity CT Scan services using the latest technology, like our state-of-the-art Siemens Force scanner. Our team of skilled technicians and radiologists offer a meticulous approach, providing clients with comprehensive, accurate, and detailed results. We also strive to improve our offerings and ensure they are cost-efficient for our clients.
DiagnostiCare offers highly personalised CT Scan services tailored to meet the unique needs of its clients, whether in Melbourne or surrounding areas like Keilor East, Airport West, and Ascot Vale. Our services include, but are not limited to, CT Coronary Angiography Melbourne and CT Coronary Angiography and Calcium Score Melbourne.
Before your CT Scan, you should avoid nicotine or caffeine 24 hours prior to the procedure. It’s also important to inform your radiologist of any existing medical conditions such as asthma or poor renal function. Prior to the scan, you’ll fill out paperwork and may be given a beta blocker to lower your heart rate, as well as a contrast fluid to highlight areas in the body for clearer imaging.
CT Coronary Angiography is an X-ray examination of the blood vessels near the heart, which provides valuable information without invasive procedures. Our CT Coronary Angiography and Calcium Score procedures in Melbourne aim to highlight calcium deposits in arteries, providing a reliable indicator of atherosclerosis and assessing one’s risk of a stroke or heart attack.
DiagnostiCare is dedicated to offering the highest standard of care using cutting-edge technology and highly trained technicians. We also offer bulk billing to enhance the accessibility of our services. Our team ensures comprehensive and personalised care for all patients. For any further assistance or inquiries about CT Scan Melbourne services, you may call us at (03) 9337 8288 or email us at info@diagnosticare.com.au.